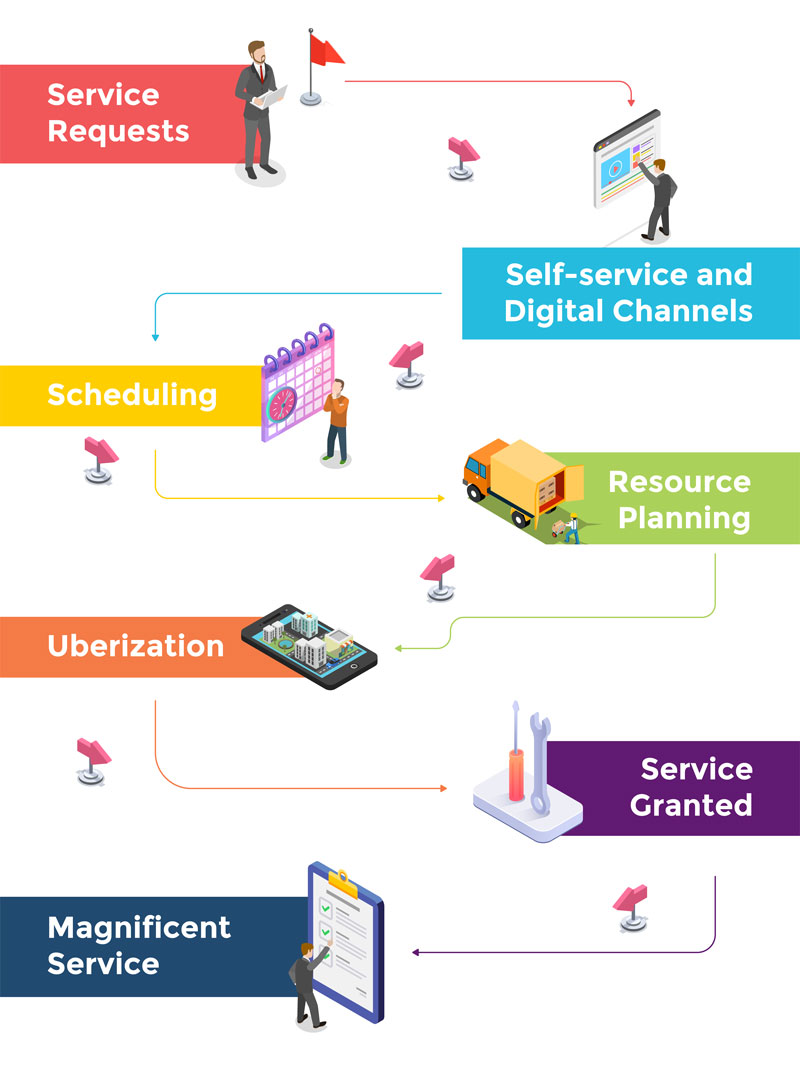
1. Service Requests
It all starts when customers make requests through different channels: CSS portals, chatbots, VPAs or just by contacting the service center. These requests can be related to the acquisition of new products and services or fixing issues related to the customer’s current services.
2. Self-service and Digital Channels
To solve customers’ requests, utilities have different alternatives. Some requests are solved immediately via chatbots, VPAs, CSS portals or other digital channels. Other times, service representatives can handle the requests and give prompt solutions and answers to customers. In some cases, it is necessary to create work orders for technicians to solve issues on the field. In these situations, different messages and proactive notifications are sent to customers to keep them well informed about jobs to be executed.
3. Scheduling
Field service activities should be performed when the customer feels its most convenient. Therefore, the utility scheduling process should be flexible and allow the utility to assign tasks based on appointments previously made and customers’ preferred time frames. It is also important to consider that unexpected events can occur at any time and need to be handled ASAP.
In addition, having coordination of materials and necessary tools is also leads to excellent scheduling.
4. Resource Planning
The distribution of orders and crew activities takes into account several factors, including the availability of resources to serve all customers and fulfill all commitments. At this point, proactive notifications are also sent to customers giving them additional information about tasks that are going to be performed.
- At this point of the journey, intelligent routing creates the most efficient routes for the crews to follow. These paths include the best way and time to pick up necessary materials without delaying the arrival time.
5. Uberization
At this stage, customers now know the necessary information and status about their orders, including the precise time of the crew arrival. Through additional proactive notifications, customers can visualize the technicians’ location on a map as well as their progress along the route. Other communication options such as chat, calls, or order rescheduling are also available for customers, offering them personalized services.
- At this point of the journey, intelligent routing allows utilities to provide reliable Estimated Times of Arrival (ETAs) to customers, which together with other proactive notifications have a positive impact on their satisfaction.
6. Service Granted
Customers’ requests are successfully handled when the technicians perform all the required tasks and the issues presented get solved.
- At this point of the journey, intelligent routing empowers utilities to assign the right technician with the right tools at the right time, enhancing customers’ experiences while optimizing resources to improve operational efficiency.
7. Magnificent Service
Possible gaps between customers’ expectations and their utility’s performance can be reduced when offering an excellent field service enhanced by intelligent routing. The main CSAT indicators including Customer Experience (CX) and Customer Engagement levels are boosted in a significant way.
- At this point of the journey, intelligent routing encourages utilities to maximize their resources and make the most out of technologies like AI to provide the best experience even when fixing issues or executing field service activities.